- Published on
System Design: Build a Database Cluster with Primary(Master) & Read Replica(Slave)
- Authors
- Name
- Loi Tran
Introduction
A common requirement for building scalable systems is creating read replicas for high availability & load balancing.
By scaling our DB horizontally we can more reliably ensure that our services don't slow down, or worse, go down.
Today we'll create a primary & replica Postgres DBs.
We'll use Docker to containerize them so we can deploy to the cloud easily.
Overview
- Setup Dockerized Repo & Primary DB:
- a. Setup repo.
- b. Define Primary Docker config files.
- c. Define Primary DB config.
- d. Define Primary Client authentication.
- e. Setup Seed Table & Records.
- f. Define Primary container/service.
- Create Dockerized Replica DB:
- a. Define Replica service.
- b. Config replica service in
./db/init-replica.sh.
- Check data replication from Master to Slave with shell or PGAdmin:
- a. Test with bash shell.
- b. Test with PGAdmin.
1. Setup Dockerized Repo & Primary DB
mkdir system_design_db_cluster
cd system_design_db_cluster
mkdir -p db/config
touch ./db/replication.sql ./db/config/postgresql.conf ./db/config/pg_hba.conf docker-compose.yml
# ./db/config/postgresql.conf
wal_level = replica
max_wal_senders = 10
wal_keep_size = 64MB
listen_addresses = '*'
primary_conninfo = 'host=primary port=5432 user=postgres password=password'
# ./db/config/pg_hba.conf
local all all trust
host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
host replication all 0.0.0.0/0 trust
# ./db/replication.sql
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Wizards (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
firstname VARCHAR(50),
lastname VARCHAR(50),
email VARCHAR(100)
);
INSERT INTO Wizards (firstname, lastname, email) VALUES
('Harry', 'Potter', 'harry.potter@hogwarts.edu'),
('Ron', 'Weasley', 'ron.weasley@hogwarts.edu'),
('Hermione', 'Granger', 'hermione.granger@hogwarts.edu');
version: '3.8'
services:
primary:
image: postgres:16
container_name: primary
environment:
POSTGRES_DB: mydb
POSTGRES_USER: postgres
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: password
ports:
- '5432:5432'
volumes:
- primary_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
- ./db/replication.sql:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/replication.sql
- ./db/config/postgresql.conf:/etc/postgresql/postgresql.conf
- ./db/config/pg_hba.conf:/etc/postgresql/pg_hba.conf
command: postgres -c config_file=/etc/postgresql/postgresql.conf -c hba_file=/etc/postgresql/pg_hba.conf
restart: always
volumes:
primary_data:
- Check you can run
docker-compose up --buildto start your container/service/primary DB.
$ docker-compose up --build
[+] Running 1/0
✔ Container primary Created 0.0s
Attaching to primary
primary | The files belonging to this database system will be owned by user "postgres".
primary |
primary | Data page checksums are disabled.
primary | Success. You can now start the database server using:
primary | pg_ctl -D /var/lib/postgresql/data -l logfile start
primary | done
primary | server started
primary | PostgreSQL init process complete; ready for start up.
primary | 2025-05-03 08:08:24.024 GMT [1] LOG: database system is ready to accept connections
2. Create Dockerized Replica DB
So now we want to create another instance of Postgres which replicates the data from our primary db.
- A. Define Replica service
- B. Config replica service in
./db/init-replica.sh.
version: '3.8'
services:
primary:
image: postgres:16
container_name: primary
environment:
POSTGRES_DB: mydb
POSTGRES_USER: postgres
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: password
ports:
- '5432:5432'
volumes:
- primary_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
- ./db/replication.sql:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/replication.sql
- ./db/config/postgresql.conf:/etc/postgresql/postgresql.conf
- ./db/config/pg_hba.conf:/etc/postgresql/pg_hba.conf
command: postgres -c config_file=/etc/postgresql/postgresql.conf -c hba_file=/etc/postgresql/pg_hba.conf
restart: always
replica1:
image: postgres:16
container_name: replica1
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: postgres
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: password
depends_on:
- primary
ports:
- '5433:5432'
volumes:
- replica1_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
- ./db/config/postgresql.conf:/etc/postgresql/postgresql.conf
- ./db/init-replica.sh:/init-replica.sh
entrypoint: /init-replica.sh
restart: always
volumes:
primary_data:
replica1_data:
#!/bin/bash
set -e
PGDATA="/var/lib/postgresql/data"
if [ -z "$(ls -A $PGDATA)" ]; then
echo "Initializing replica via pg_basebackup..."
mkdir -p /tmp/pgdata
chown postgres:postgres /tmp/pgdata
su - postgres -c "pg_basebackup -h primary -D /tmp/pgdata -U postgres -Fp -Xs -P -R"
echo "Copying to PGDATA volume and fixing permissions..."
cp -a /tmp/pgdata/. "$PGDATA/"
chown -R postgres:postgres "$PGDATA"
fi
echo "Starting replica PostgreSQL..."
exec docker-entrypoint.sh postgres -c config_file=/etc/postgresql/postgresql.conf
C. Grant permissions on init file, .db/init-replica.sh.
chmod +x .db/init-replica.sh
3. Check data replication from Master to Slave with shell or PGAdmin
A. Restart docker container.
docker-compose down -v
docker-compose up --build
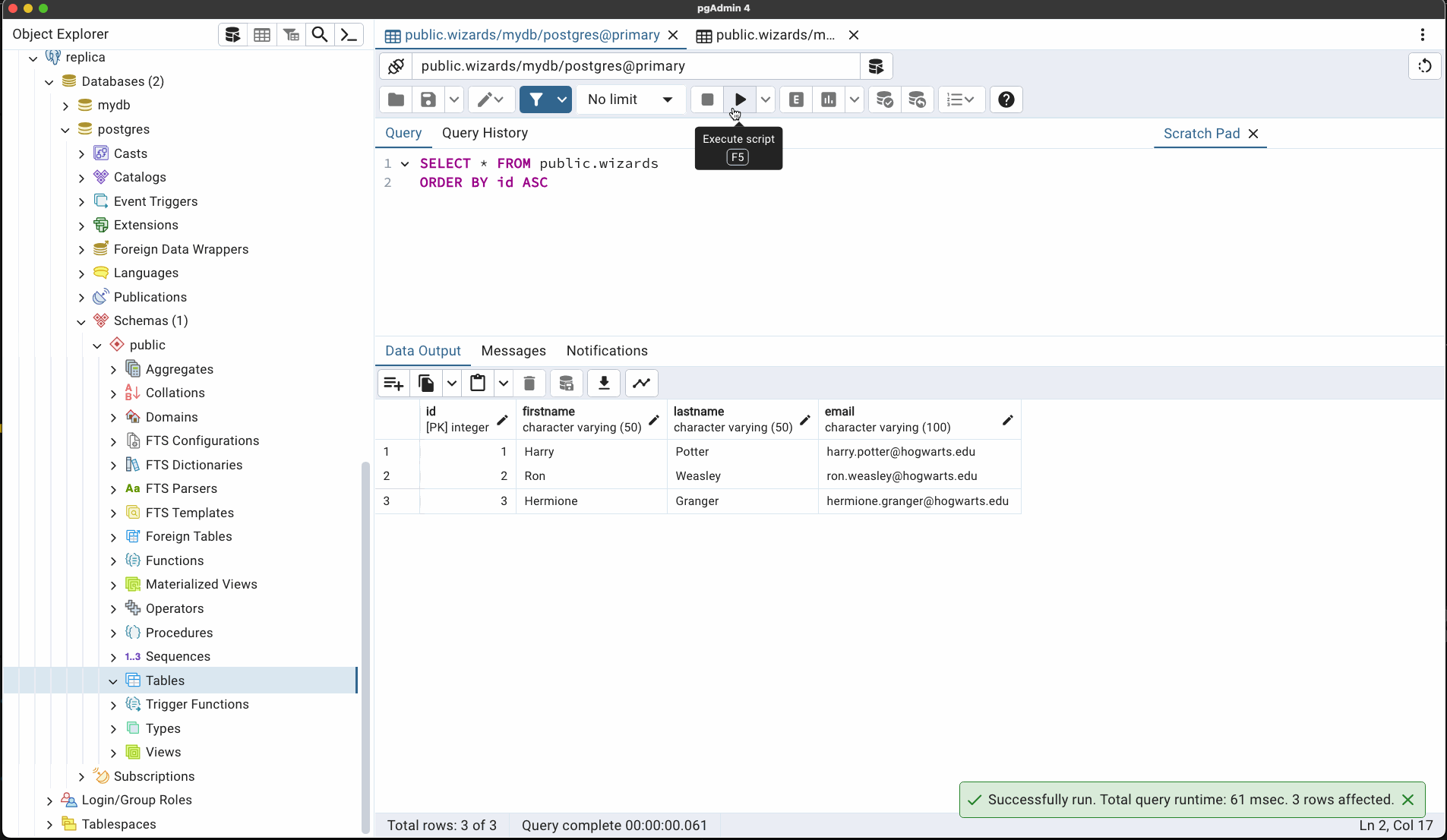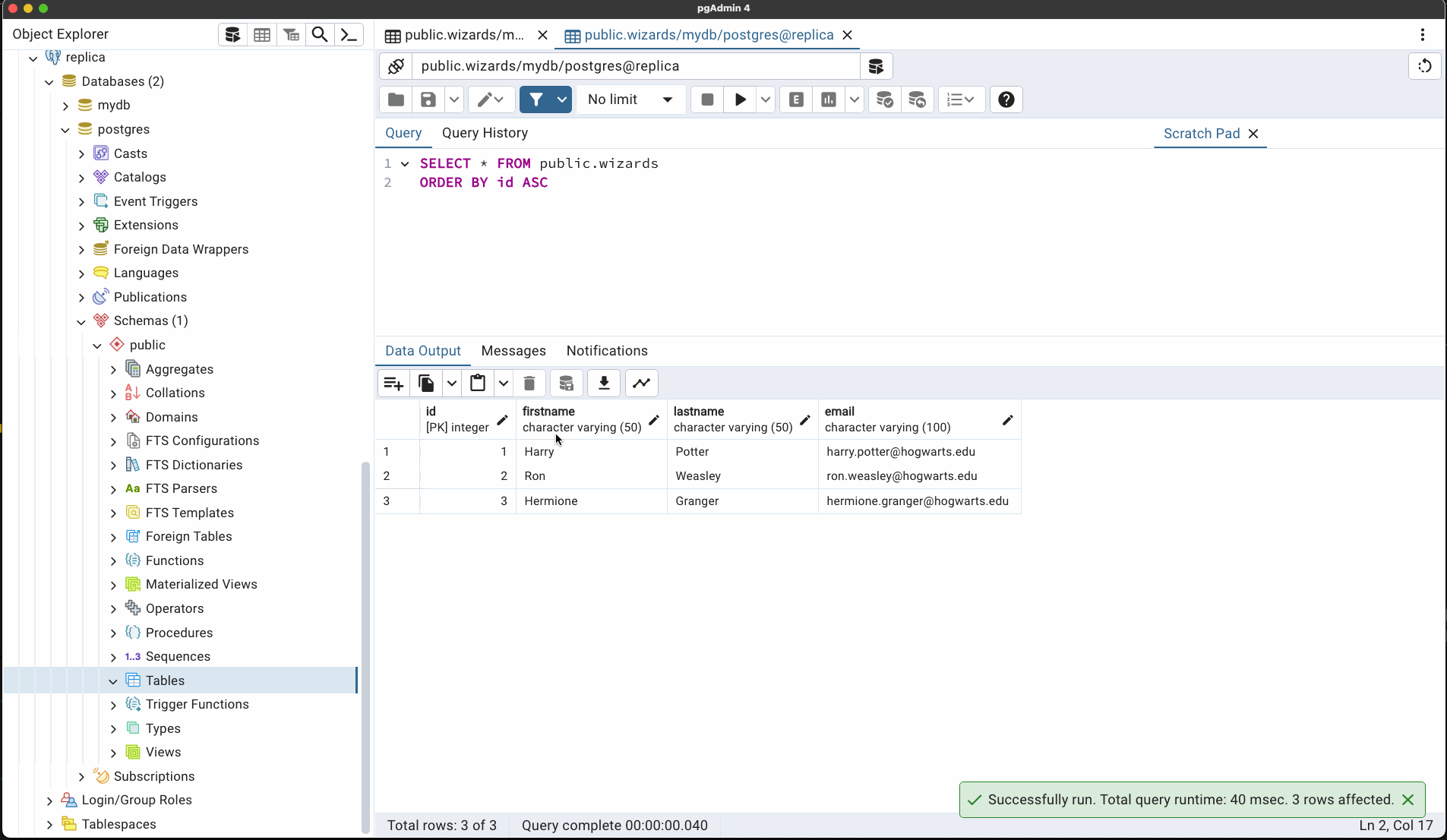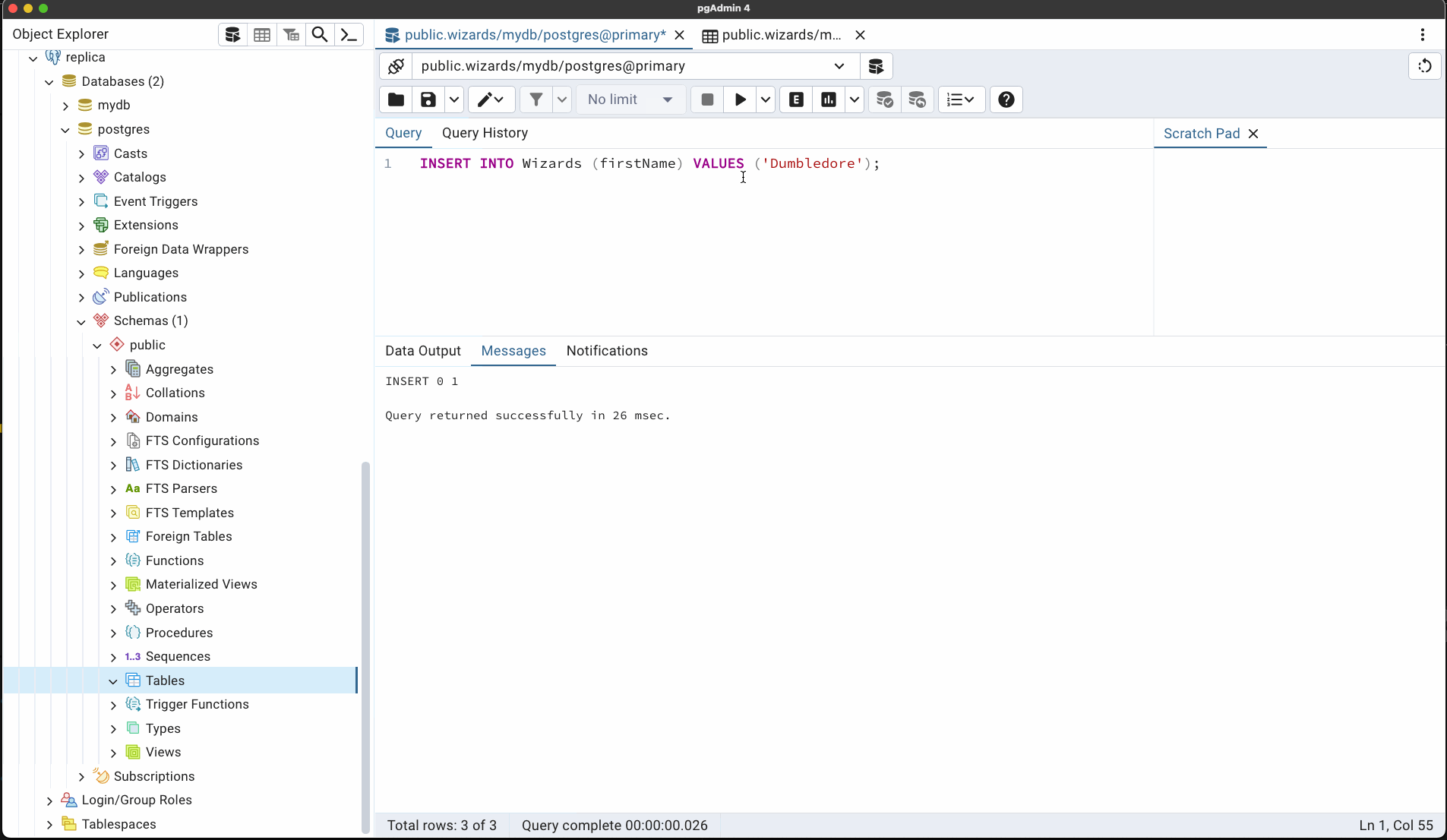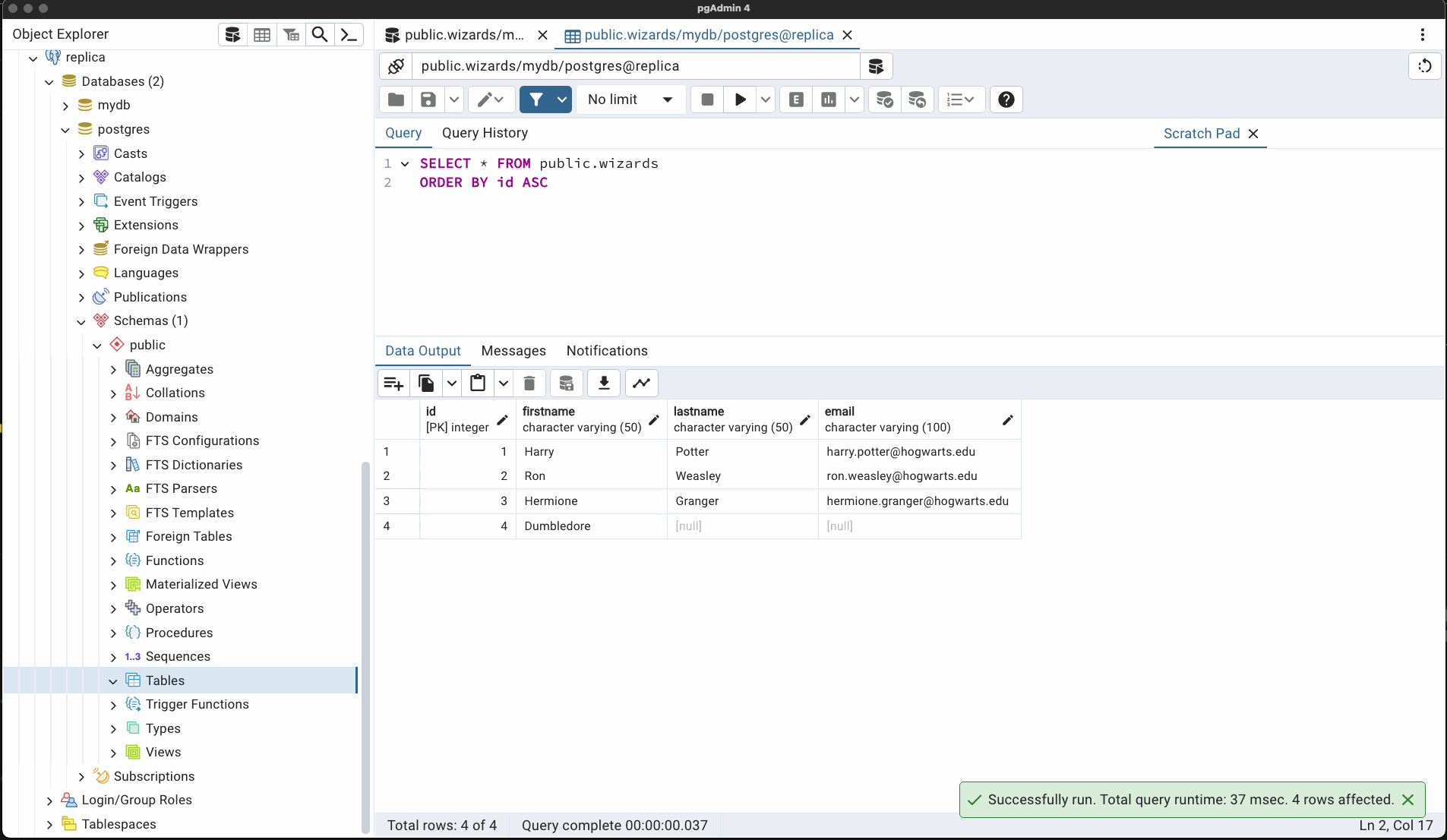
B. Connect to primary DB container & postgres using bash shell. Check to make sure the Wizards table is defined with \dt.
$ docker exec -it primary psql -U postgres -d mydb
psql (16.8 (Debian 16.8-1.pgdg120+1))
Type "help" for help.
mydb=# \dt
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+---------+-------+----------
public | wizards | table | postgres
(1 row)
C. Connect to replica1 DB container.
$ docker exec -it replica1 psql -U postgres -d mydb
D. Write to primary DB.
INSERT INTO Wizards (firstName) VALUES ('Merlin');
E. Check replica1 DB copies records from primary.
SELECT * FROM Wizards;
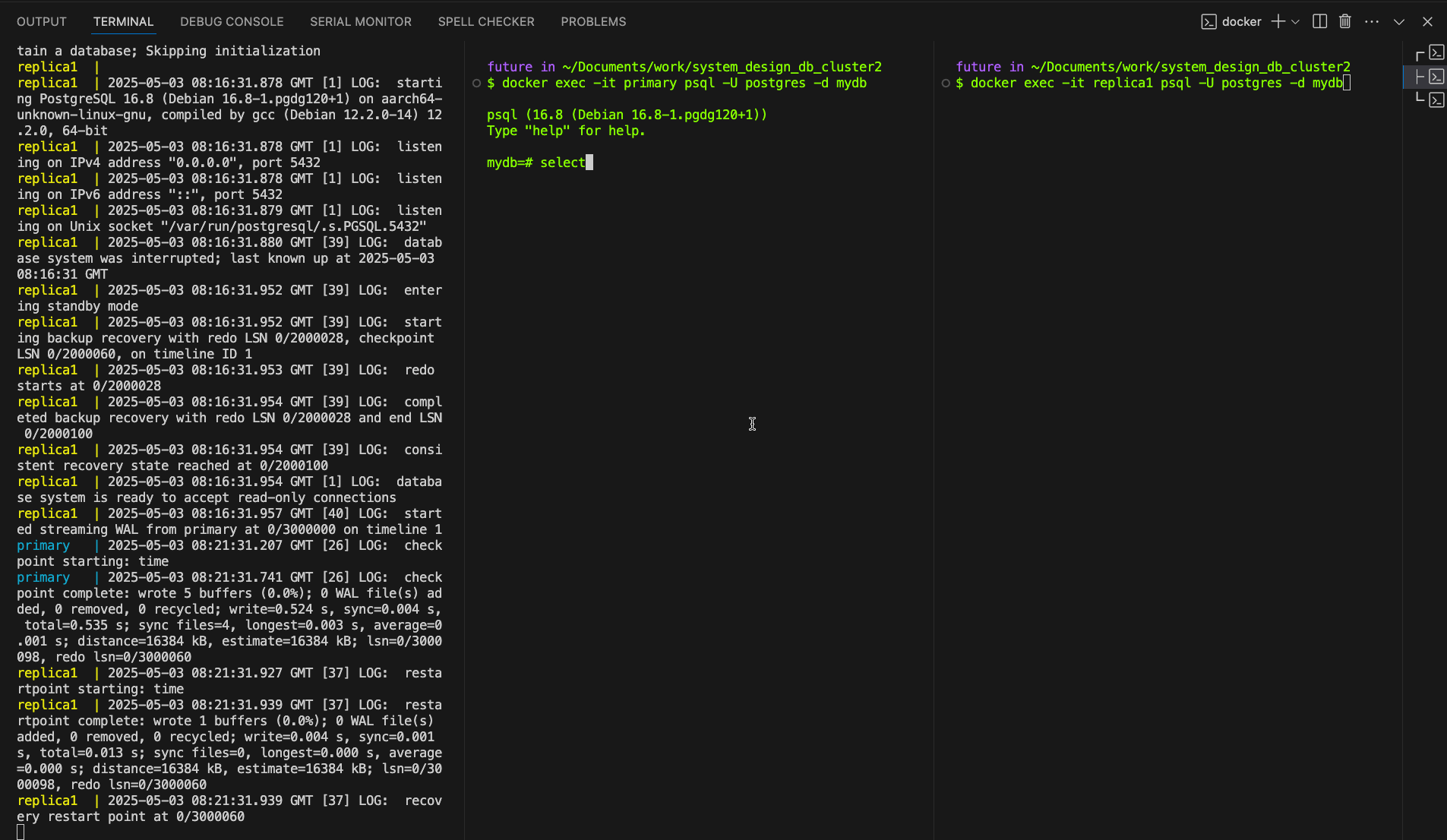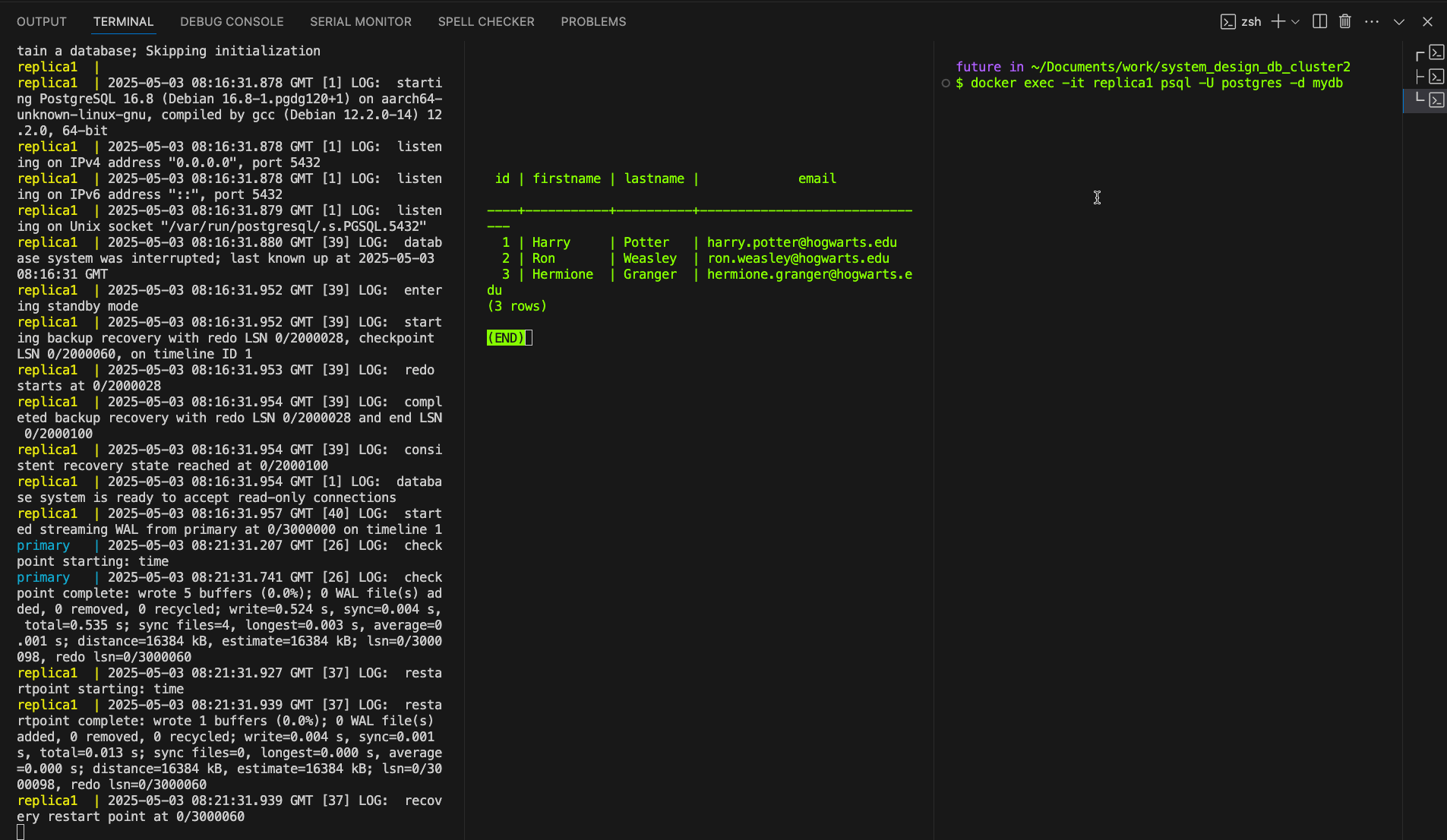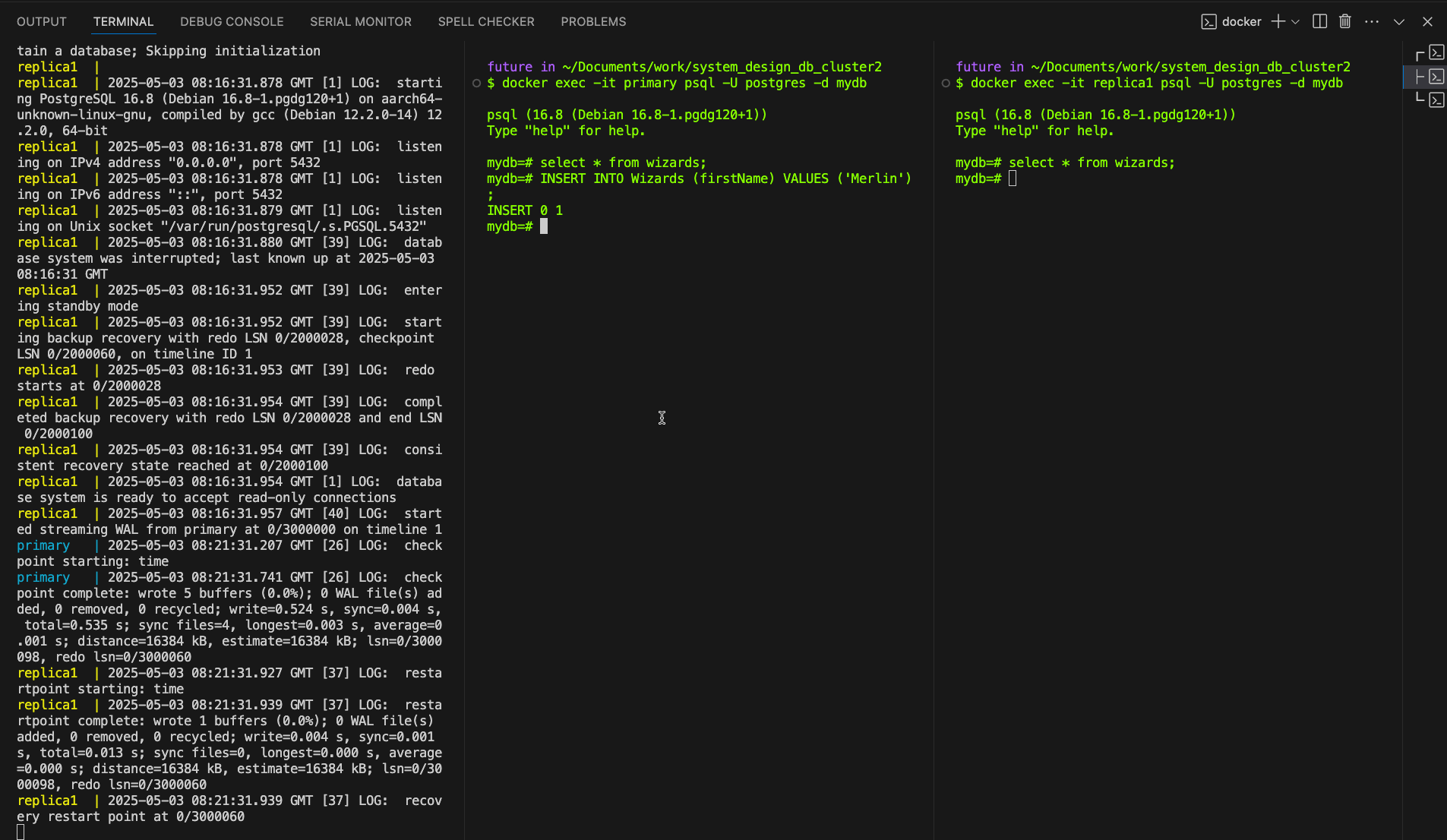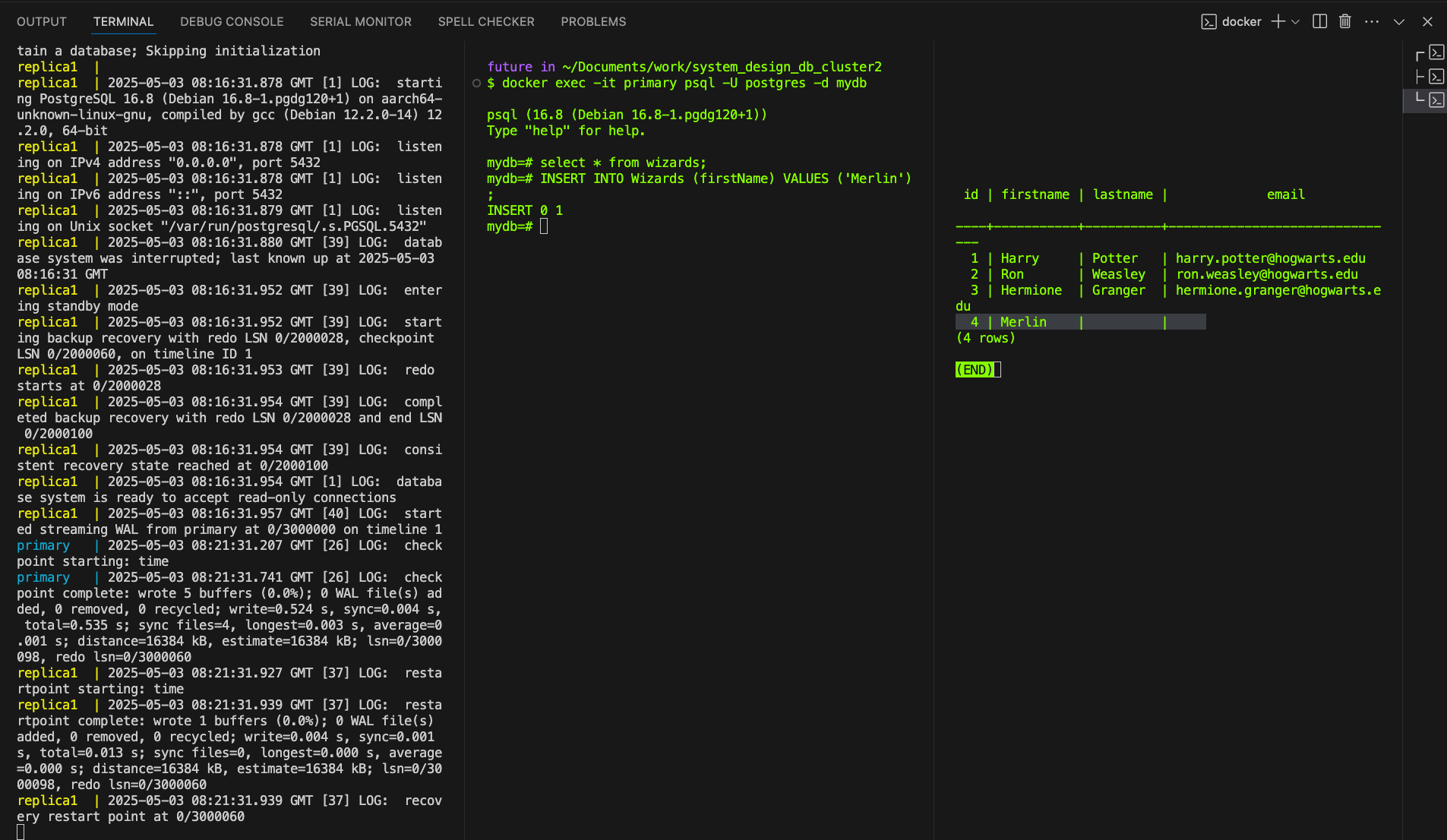
Alternatively use PGAdmin, create 2 server connections, and view your tables & schemes in each DB instance.
